[ad_1]
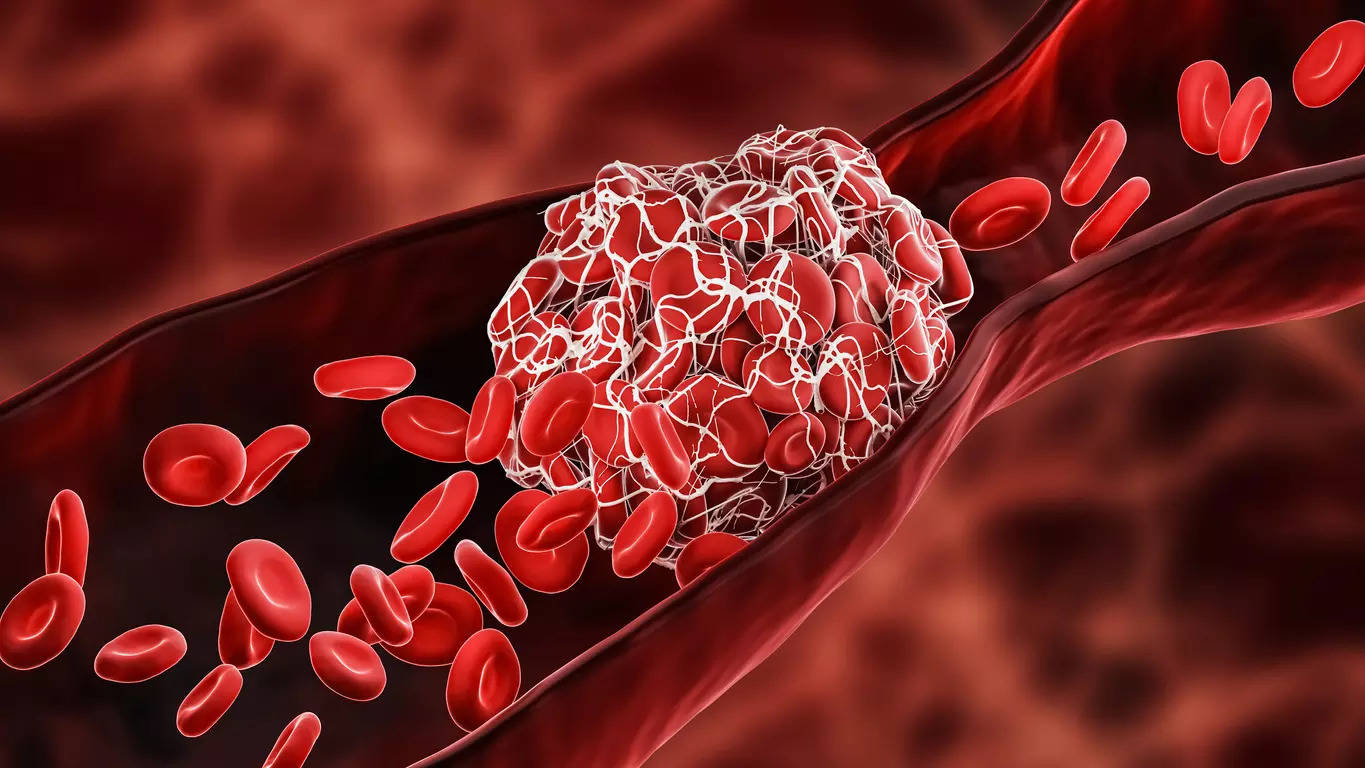
New Delhi: COVID-19 an infection will increase the chance of doubtless life-threatening blood clots by at the very least 49 weeks, or virtually a yr, even in people who find themselves not hospitalized. happen, researchers warn.
Findings counsel that the pandemic might have led to a further 10,500 circumstances of coronary heart assault, stroke, and different blood clot issues in England and Wales in 2020 alone, though the extra danger for people stays small and reduces over time. it occurs.
Associated information

Research makes a mind-boggling discovery, establishing a hyperlink between sleep, desires and dementia

surprising! This gene, discovered in additional than 230 million individuals globally, might improve the chance of demise from COVID – do you may have too?
The authors counsel that preventive methods, akin to giving high-risk sufferers low blood stress treatment, might assist cut back circumstances of extreme clots, in response to a research of the well being data of 48 million illiterate adults from the primary wave of the pandemic. . Journal circulation.
Within the first week after a COVID-19 analysis, individuals had been 21 occasions extra prone to have a coronary heart assault or stroke, situations which are primarily brought on by blood clots blocking arteries.
Associated information

Dad and mom, beware! Research have discovered that MSG or ajinomoto, which is often utilized in Chinese language meals, may cause poisonous results in infants and rising fetuses.

Specialists say that consuming on time regulates mind well being
That is 3.9 occasions extra prone to happen after 4 weeks.
The researchers additionally studied situations brought on by blood clots within the veins: these embody deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism – a clot within the lungs that may be deadly.
The chance of blood clots within the veins was 33 occasions greater within the first week after a COVID-19 analysis. It got here all the way down to an eight-fold greater danger after 4 weeks.
A lot of the earlier analysis has studied the impact of COVID on blood clotting in hospitalized individuals.
The brand new research exhibits that there was an impression even in individuals whose covid didn’t hospitalize, though their extra danger was not as nice as for many who had extreme sickness and had been hospitalized.
Disclaimer: This story has been revealed from a newswire service and has been modified by Instances Now to nothing however the headline.
[ad_2]
Supply hyperlink